题目
给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
如果字符串的反序与原始字符串相同,则该字符串称为回文字符串。
示例 1
输入:s = "babad"
输出:"bab"
解释:"aba" 同样是符合题意的答案。
示例 2
输入:s = "cbbd"
输出:"bb"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000s仅由数字和英文字母组成
分析
- 可以暴力求解
- 求最值问题 可以 动态规划
- 字符串问题 也可以滑动窗口
解题
暴力法
我自己的最开始的写法 感觉还需要训练
def solution(s: str):
"""
1.双重循环
"""
result = ''
total_length = len(s)
def vaild_is(current_index: int, s: str, check_dp: bool):
left_index = current_index - 1
right_index = current_index + 1
tmp_rst = s[current_index]
if check_dp:
if (right_index < total_length and tmp_rst == s[right_index]):
"""
1. a bb a
"""
tmp_rst = tmp_rst + s[right_index]
if right_index >= total_length:
return tmp_rst
# 一种加 一种不加
right_index += 1
if left_index < 0 or right_index >= total_length:
"""
1. 第一位开始时候 left 到了 -1
"""
return tmp_rst
while right_index < total_length and left_index >= 0:
if s[left_index] == s[right_index]:
tmp_rst = s[left_index] + tmp_rst + s[right_index]
else:
break
left_index -= 1 # 扩散+1
right_index += 1 # 扩散+1
print('tmp_rst', tmp_rst)
return tmp_rst
for index in range(0, total_length):
tmp_cs_1 = vaild_is(index, s, False)
tmp_cs_2 = vaild_is(index, s, True)
print(index, "tmp_cs_2", tmp_cs_2, "tmp_cs_1", tmp_cs_1)
tmp_cs = len(tmp_cs_2) > len(tmp_cs_1) and tmp_cs_2 or tmp_cs_1
if len(tmp_cs) > len(result):
result = tmp_cs
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
c = solution("aacabdkacaa")
print(c)
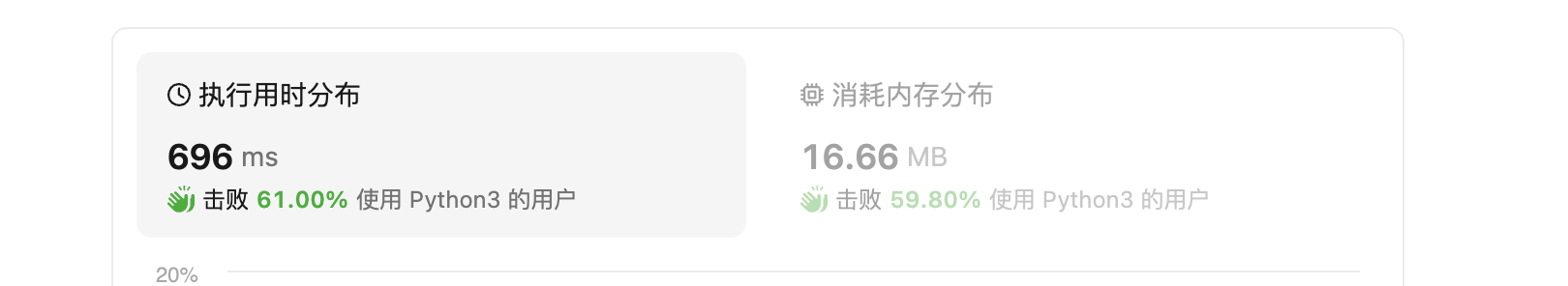
暴力解题的难点 在于边界处理 我写这个错了好多遍 上面的
tmp_cs_1 = vaild_is(index, s, False) tmp_cs_2 = vaild_is(index, s, True)有优化空间 可以先判断 是不是 dd 类型
def solution(s: str):
total_len = len(s)
if total_len <= 1:
return s
rst = s[0]
tmp_max_len = 1
def vaild(ts: str, left_index: int, right_index: int):
"""
往中间计算
"""
while left_index <= right_index:
if ts[left_index] != ts[right_index]:
return False
left_index += 1
right_index -= 1
print('s',left_index,right_index)
return True
for i in range(0, total_len):
for j in range(i + 1, total_len):
sub_str_length=j-i+1
if sub_str_length > tmp_max_len and vaild(s, i,j):
print(sub_str_length)
tmp_max_len = sub_str_length
rst = s[i:i+tmp_max_len]
return rst
if __name__ == '__main__':
c = solution("aacabdkacaa")
print(c)
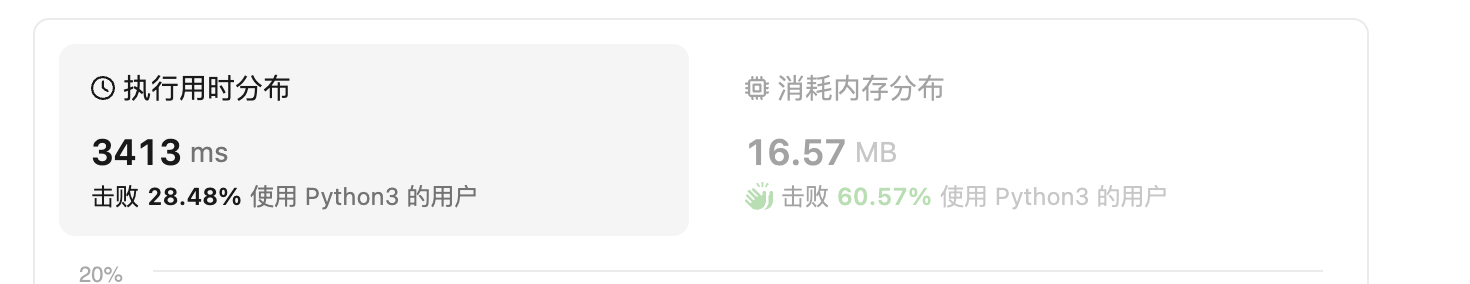
动态规划法
确定状态
状态用一个二维数组描述
确定转换方程
problem[left_i] == problem[right_j] and (right_j - left_i <= 2 or dp[left_i + 1][right_j - 1])
求解函数
确定遍历顺序 和结果构造
def solution(s: str):
"""
1. 子问题
"""
str_length = len(s)
rst = s[0]
max_length = 1
global_map = {
'rst': rst,
'max_length': max_length
}
if str_length <= 1:
return s
def initialize_dp(problem):
"""
dp[left][right]=True 表示是一个回文字符串
"""
problem_length = len(problem)
return [[False for i in range(0, problem_length)] for j in range(0, problem_length)]
def stats_transition(dp, left_i, right_j, problem, global_map):
"""
内面的是回文字 无需再判断
"""
if problem[left_i] == problem[right_j] and (right_j - left_i <= 2 or dp[left_i + 1][right_j - 1]):
dp[left_i][right_j] = True
cur_length = right_j - left_i + 1
if cur_length > global_map['max_length']:
global_map['max_length'] = cur_length
global_map['rst'] = problem[left_i:right_j+1]
def construct_result(dp, problem, global_map):
"""
"""
return global_map['rst']
dp = initialize_dp(s)
"""
确定遍历顺序
保证 所有都是经过计算的, 需要先计算
1. 从被依赖的计算
"""
for i in reversed(range(0, len(dp))):
for j in range(i,len(dp)):
#print('i,j',i,j)
stats_transition(dp, i, j, s, global_map)
#print(dp)
solution = construct_result(dp, s, global_map)
return solution
if __name__ == '__main__':
c = solution("aacabdkacaa")
print(c)
print('exit')
中心扩展法
manacher
manacher 方案 感觉不通用 先不看